Project: UAV Optimization
In this project I needed to create a MATLAB script that would be able to find the optimal dimensions for a UAV under prescribed conditions. The general philosophy of this project was to use MATLAB to "brute force" the best dimensions for our aircraft. To accomplish this, I first needed to make a function that could calculate the performance specs of an airplane. After that, another script will generate 100,000 aircraft with randomized dimensions and call the first function to identify the best one.
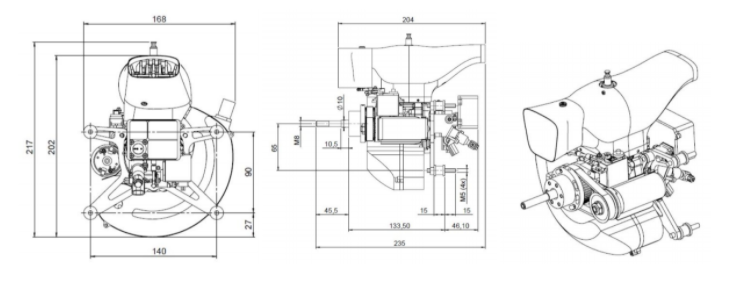
First, I found an engine that would realistically be used on an aircraft in the size range I would be using. For this, I chose the RCV DF35 Single Cylinder UAV Engine 4-Stroke Engine. This engine has a maximum power output of 3.4 horsepower and weighs around 5 pounds. Throughout every iteration, it is assumed that this is the engine being used.
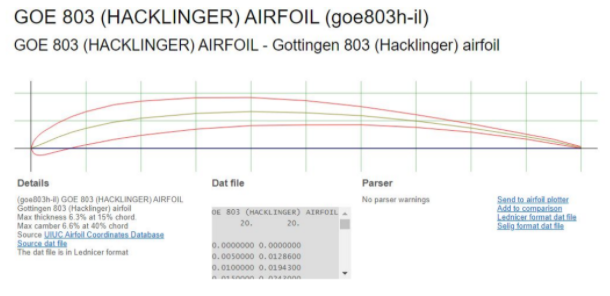
 In my case, the UAV will need to have a long hang time and a high margin of stability. For this reason, I chose to use the GOE 803 Airfoil due to it's high camber profile which is ideal for producing large amounts of lift in low speed conditions.
In my case, the UAV will need to have a long hang time and a high margin of stability. For this reason, I chose to use the GOE 803 Airfoil due to it's high camber profile which is ideal for producing large amounts of lift in low speed conditions.
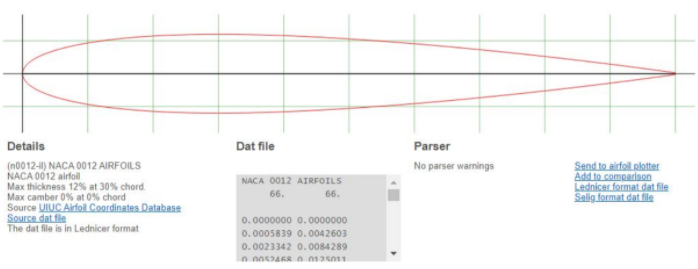
 Additionally for the tail, I wanted a neutral camber profile so I chose the NACA-0012 Airfoil. The centroids and specs of these two wing profiles were used for all calculations.
Additionally for the tail, I wanted a neutral camber profile so I chose the NACA-0012 Airfoil. The centroids and specs of these two wing profiles were used for all calculations.
 The next step was to create a series of functions that will calculate the performance specs of an aircraft based on the input dimensions. Using the Nicolai Equations, the first MATLAB function returns a converged estimate of the necessary weights for an aircraft of the input dimensions.
The next step was to create a series of functions that will calculate the performance specs of an aircraft based on the input dimensions. Using the Nicolai Equations, the first MATLAB function returns a converged estimate of the necessary weights for an aircraft of the input dimensions.
 Once the Nicolai function has run, the outputs are fed into another function that will find the Center of Gravity of the plane, as well as the margins of stability. Ideally, since this UAV will need to be very stable, we want the static margin to be between 0.10 - 0.30.
Once the Nicolai function has run, the outputs are fed into another function that will find the Center of Gravity of the plane, as well as the margins of stability. Ideally, since this UAV will need to be very stable, we want the static margin to be between 0.10 - 0.30.
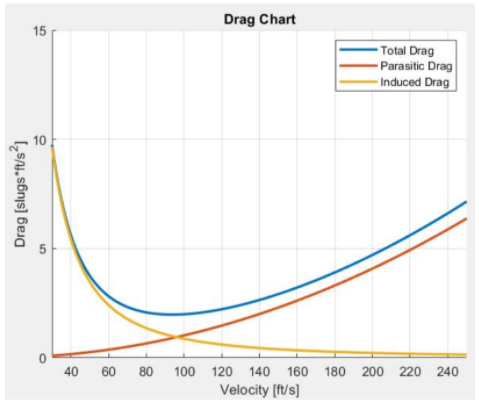
 Finally, we are ready to find the specs of the aircraft. The next function will use several loops and equations to find everything we need including: parasitic, induced, and total drag, maximum coefficient of lift, maximum velocity, stall speed, cruising speed, range, and endurance. This is done by finding the drag of each component and summing them in addition to an interference factor. On the below chart, you will see that the cruising speed occurs where total drag is at a minimum. This cruising speed is multiplied by the fuel consumption rate to find the endurance of the aircraft.
Finally, we are ready to find the specs of the aircraft. The next function will use several loops and equations to find everything we need including: parasitic, induced, and total drag, maximum coefficient of lift, maximum velocity, stall speed, cruising speed, range, and endurance. This is done by finding the drag of each component and summing them in addition to an interference factor. On the below chart, you will see that the cruising speed occurs where total drag is at a minimum. This cruising speed is multiplied by the fuel consumption rate to find the endurance of the aircraft.
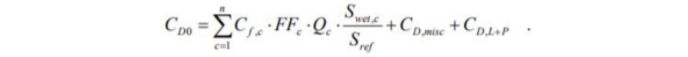
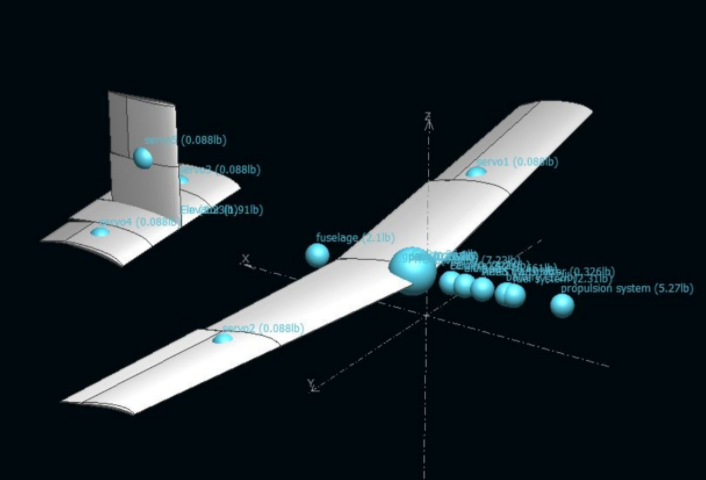
 Now that we have everything needed to find the specs of an input aircraft, the main script generates 100,000 randomized aircraft and tests each one. At the end of the run, the best dimensions are saved and we can generate a 3D model based on the results.
Now that we have everything needed to find the specs of an input aircraft, the main script generates 100,000 randomized aircraft and tests each one. At the end of the run, the best dimensions are saved and we can generate a 3D model based on the results.
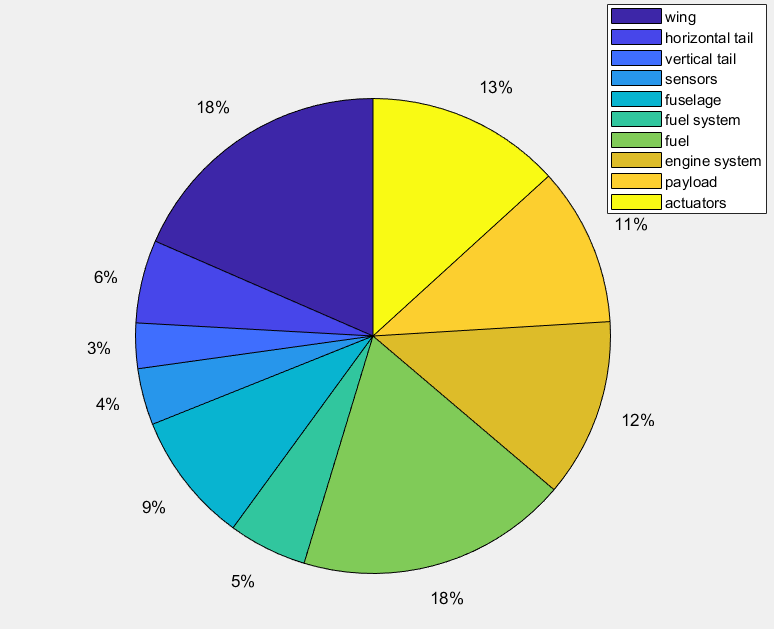
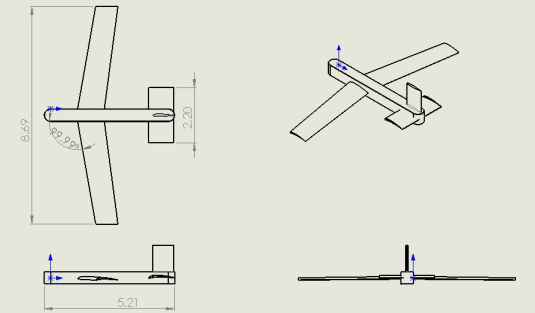 Using the engine prescribed and only 1.2 gallons of fuel, this optimized aircraft is able to stay in the air for a theoretical maximum of 29 hours at 15,000 feet. Additionally, the aircraft has a range of over 1,500 miles at a cruising velocity of 73 ft/s. The total weight of this UAV, including the chosen electrical equipment, fuel, and sensors came out to 36.4 pounds.
Using the engine prescribed and only 1.2 gallons of fuel, this optimized aircraft is able to stay in the air for a theoretical maximum of 29 hours at 15,000 feet. Additionally, the aircraft has a range of over 1,500 miles at a cruising velocity of 73 ft/s. The total weight of this UAV, including the chosen electrical equipment, fuel, and sensors came out to 36.4 pounds.